A Patient with lack of resolution of persistent cough, shortness of breath and now complains of Lack of appetite
The complete case can be found here
https://a-blog-by-adityarayilla.blogspot.com/2020/06/left-sided-pleural-effusion-case.html?m=1
What are the possible differential diagnoses?
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)asthma,
pulmonary fibrosis
Congestive heart failure
pulmonary thromboembolism
pneumonia
neuromuscular disease
left pleural effusion
points in favour and against each diagnosis at this point of time.
pleural effusion
heaviness on left side
cheast pain
shortness of breath
decrease breath sounds on left side
congestive heart failure
pedal edema
dyspnea
decreased urine output
against: no orthopnea or PND
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
dyspnea
beedi smoker
pneumonia
dyspnea
against: patient is afebrile
pulmonary thromboenbolism
dyspnea
against: not sudden oncet, no embolic risk factors
renal failure
reference: davidson principles and practice of medicine chapter on respiratory medine
Out of all differential diagnoses, most likely is.
pleural effusion is most likely as heaviness is classic of pleural effusion
More information about history and examination to reach the final diagnosis
diffrential diagnosis for left sided pleural effusion include
Pneumonia (‘parapneumonic effusion’)
any history of fever
Tuberculosis
socioeconomic status of patient
family history of TB
Subdiaphragmatic disorders (subphrenic abscess, pancreatitis etc.)
abdominal pain
Malignant disease
weightloss - loosening of clothes
previous diagnosis of malignancy
smoking
nephrotic syndrome - CKD
JVP
any pleural friction rub
brown line on nails
signs of perepheral neuropathy
easy brusing
pruritus
preitoneal dialysis catheter
Post-myocardial infarction syndrome
history of angina
Asbestos-related benign pleural effusion
history of work in asbestos industry
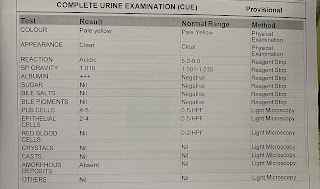
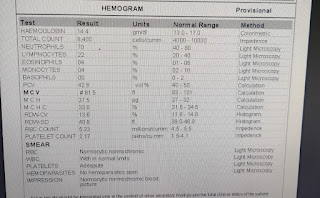
Investigations
Chest xray, CT chest
evaluate TB
evaluate pleural effusion
evaluate pneumonia
evaluate COPD
renal function tests
confirm CKD
pleural tap
find the cause weather it is exudative or transudative effusion
LFT, complete haemogram
Diagnosis
Chest xray shows oblitration of costo diaphragmatic angle and fluid level on left side suggesting pleural effusion.
HRCT shows, endobronchial infection on left side and chronic kidney disease at left kidney
pleural tap analysis
high lumphocyte count and high protien suggests tubercular pleural effusion
reference: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6542220/
davidson table 15.29
final diagnosis
pulmonary tuberculosis with CKD
Treatment
anti tubercular treatment

Comments
Post a Comment